There are a number of free network scanner tools, apps and utilities for Mac OS X if you’re looking to monitor the devices connected to you LAN or even the specific packets that are traveling to and from your LAN. In the video above, I go over 5 different tools that you can use to monitor your network traffic on a Mac OS X computer. Free IT Monitoring & Analysis Tools 100% Free. Permissions Analyzer for Active Directory. Construct and test your network in a risk-free virtual environment. GNS3 Network Emulator. DOWNLOAD FREE TOOL 100% Free EMAIL LINK TO FREE.
- Free Network Monitoring Tools For Mac Os
- Free Network Monitoring Tools For Macbook Pro
- Network Tools For Mac
In the last few years, networking monitoring tools are in a state of constant growth. Today we have the best network monitor tools with the quality for Windows and Linux OS. And there is a demand for open-source network monitoring with network scanning, network monitoring and SNMP integration combined, which is good news for administrators. At present, many network monitoring tools provide a real-time breakdown of your live network.
Network monitoring is a place where you will find many tools. So we have found the best network monitoring software for you. Here you will find paid, free, and open-source software for Windows, Mac, and Linux OS.
In this article, we’ve prepared a list of the best network monitoring software on the market. Every tool listed here is suitable for the business environment. We have paid attention to various features and key differentiators like real-time network monitoring, notifications, alerts, visualization, custom configurations, and topology mapping.
Recommended: Best IT Help Desk Software
Best Network Monitoring Software & Tools
Contents
- 1 Best Network Monitoring Software & Tools
- 1.12 #12. EventSentry
#1. Obkio Network Performance Monitoring
Obkio is the simplest network performance monitoring SaaS solution that empowers users with end-to-end visibility of the network performance. With quick and easy installation, users can start monitoring network performance within minutes, with access to Obkio’s sleek, user-friendly interface.
No one can afford network slowdowns – that’s why Obkio continuously monitors the health of network and core business applications to improve the end-user experience and identify the cause of intermittent network, VoIP, video, device, and applications slowdown in seconds.
Easily view all network alerts and metrics on Obkio’s customizable dashboard, complete with Obkio’s innovative chord diagram.
Obkio’s solution consists of deploying software or hardware network monitoring Agents at strategic locations in a company’s offices, branches and other network destinations to monitor network performance in a distributed, decentralized manner. It continuously measures network performance, collects data, and automatically alerts users of any network performance problems.
Obkio continuously tests and measures different operating parameters based on network metrics, such as latency, jitter, packet loss, quality of service and customer experience via the QoE (Quality of Experience) and performs speed tests regularly to check whether the data available coincides well with what should be offered by service providers.
With Obkio’s Network Device Monitoring solution, monitor the health of network devices such as Firewalls, Routers, Switches, Wi-Fi APs and any SNMP-enabled devices.
Try Obkio for free with a 14-day trial, with access to all of Obkio’s premium features. Users can also choose from a variety of free and paid plans tailored to their needs.
#2. Checkmk
Checkmk is a universal monitoring tool with great capabilities for monitoring your network devices. The Checkmk Raw Edition is completely open-source and offers free and unlimited monitoring. The Checkmk Enterprise Edition comes with additional functionalities.
The tool supports monitoring via the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), but it also comes with more than 1,900 preconfigured plug-ins for vendors such as Cisco, Brocade, Dell, Huawei, Intel, Juniper, TP-Link and many more. The integrations make the monitoring very efficient and allow you to track more assets with less hardware resources while getting more insights. One Checkmk instance can monitor thousands of devices and can easily scale horizontally thanks to the Checkmk distributed monitoring setup.
Due to the intelligent auto-discovery function, it takes you less than 15 minutes to set up a monitoring for your network. The graphical user interface of Checkmk makes managing your monitoring simple and allows you to create precise visualizations.
You can create high-level overviews or detailed network mappings with just a few clicks. You can also create individual dashboards and access rights for different users, for example, high-level overviews for the C level of your organization, or detailed insights into one device or segment for IT specialists working in the field. Checkmk also supports network flow monitoring, so you and your colleagues can see even more details, if necessary.
Thanks to the rule-based concept for configuring your monitoring, Checkmk is especially powerful when monitoring a large number of similar devices, in contrast to a template-based approach, in which you need to configure each ‘sensor’.
#3. SolarWinds
SolarWinds network monitoring software is the first name of our list. It is a top range software that tracks all of your network elements via the SNMP-Simple Network Management Protocol and a centralized dashboard. Whether you are running a wired or wireless network, you can use this network to find the signs of poor performance.
It is easy and effortless to use. SolarWinds gives you a diverse range of visual elements like maps, pie charts, and warnings for the network performance. For example, it highlights all the network element that has problems of Nodes with window. Or the Application Health Overview shows you the health of the overall section across your whole network.
The auto-discovery feature manually locates the devices on your network and outlines them to your system. So it saves the time that you spend on manually linking the network devices to the central device.
The comprehensive but straightforward design of SolarWinds is one of the plus points that makes it the best network monitor software. However, it has much more to offer like create customized alerts for network faults. Even you can allocate the alert to a specific person of the group with this software. It is useful in circumstances where you want to transfer the task to the team member. The reason why it is top of our list is it is a perfect blend of handiness and network monitoring. Another two stands out features are the auto-discovery feature and high-level visualization. It is available from $2,895 upwards. To check out the software, it gives you a 30-day free trial.
#4. Paessler PRTG Network Monitor
Paessler PRTGPRTG Network Monitor is another network management tool that gives you excellent monitoring features. PRTG uses Simple Network Management Protocol, packet sniffing, and Windows Management Instrumentation to monitor network devices.
However, it is simple to use. It also has its auto-discovery feature which works as a network mapper and identifies network elements without configuring them manually. It also reduces manual labor. Once you start using it from a pc or mobile, it starts monitoring your network via the PRTG app.
One of the first things that you notice is it is difficult to maintain the record; it is not clear. But it gives you sufficient information it has enough depth to give you a clear picture if you continue beyond the initial clunkiness and familiar with it.
PRTG maps offer visual offerings. And maps are used in many ways. The simplest way to create the map is to create a map and denote each device on your network. However, you can customize it and set it to show the most critical sensor of the network. You can also set automatic map rotation, and you can change the map view from 10 seconds to 10 minutes.
Though to use it, you have to get used to it, but it is perfect for the one who is new to network monitoring. With the learning curve, the additional features like auto-discovery, alerts, and visual displays make it better to use. It has some pricing options according to use. It can works on up to 100 monitors to the XL5 package for $1,400. The XL1 package gives you the best value for money by providing unlimited sensors for $13,436. It also provides you a trial version, and it remains free up to 100 Sensors.

#5. ManageEngine OpManager
ManageEngine OpManager is a user-friendly network management solution used by over 1,000,000 IT Admins worldwide. With real-time monitoring, customizable dashboards for a network with servers, routers, switches, ports, WLCs, firewalls, LANs, and IPs. With the rule-based discovery, custom notification profiles, workflow automation, OpManager ensures your network is up and running 24/7. OpManager monitors VMware, Hyper-V, Xen, and Nutanix server environments. All this and seamless integration with other tools makes OpManager a single stop shop for network monitoring.
The greatest asset of OpManager is a visualization by which you can get a view, graphs, dials, charts, and color-coded availability via the dashboard. You can also create custom reports. The heart of OpManager’s functionality is customization. User-configurable notifications are part of this comprehensive design.
The scalability of this best network monitoring tool is such that it is suitable for any organization from small to large enterprises. For 10 devices the price is $245 for the essential edition, and for 250 devices the price is $11,545 for the enterprise edition. A free version for three devices, two users, with basic monitoring functionality is also available. You may check for a price quote.
#6. Zabbix
Zabbix is an open-source software that comes into action once you launch it. As you launch the GUI, you can see the user-friendly design of the software. You can access almost all web browsers like Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Internet Explorer, and Google Chrome.
It works well on customization. The user configuration can send through email or SMS. Throughout your network, you can run scripts from the device or remotely. It is useful particularly when you need quick action like performance issues.
Zabbix uses SNMP and IMPI in combination to control your network. You can use it to look at the network bandwidth, network health, device utilization by memory or CPU, and configuration changes.
You will receive a message in the message window if there is any network issue with all of the detail. It is one of the network management tools which has an extensive range of templates to monitor devices. It has templates of companies like Intel, Dell, Netgear, Cisco, Huawei, and Nokia Networks devices. And all of the templates come with triggers, the scenario of the vendor device, default applications, and graphs.
Overall Zabbix is the best network monitoring software for medium to large businesses. It is available for free and accessed as a web interface. One can also download it for Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Linux, CentOS, Oracle, Ubuntu, and Debian.
#7. Nagios XI
Nagios XI, a network monitoring software tool that is known for its wide demographic data. For those who want a low maintenance solution, it is best for them. It uses a web-based user interface which makes it more accessible. Configuration wizards set up your monitoring network as well as manage your service quickly.
The visualization of the software is extensive, including graphs and pie charts displaying network performance. It also has the capacity for planning graphs. With these graphs, you can plan your IT infrastructure for the future with long-term uptime and as per your needs.
multi-tenant access is a unique feature provided by Nagios XI. It let multi-user access to sections of network infrastructure and let the user see authorized devices. It is useful in large organizations where there are many staff members, and each has a different duty to handle. It operates on Redhat Enterprise Linux or CentOS. You will get the standard edition for $1,995 and the enterprise edition for $3,495. The free version is also available to monitoring seven nodes.
#8. Icinga
Icinga is another relatively well-known network monitoring software product. It uses direct monitoring and SNMP to gather all usage data from each device that is active on a system. The major processes conducted through the REST API. The entire user interface secured with SSL. It gives the power to the user to update their configurations and view information about existing problems. Many large companies use this product like Audi, Adobe, and Vodafone.
Icinga’s user interface is relatively clean. It is plugins that make a stand out Icinga. It provides you with many plugins that conduct various monitoring tasks. Even for Windows and Linux, they have unique plugins. You can also build your plugin also from scratch.
The alert system of the software notifies the user via SMS or test so that you can reach your environment even though you are not monitoring t directly. Icinga can segment the alerts and send them to a specific user only. In short, these network performance monitoring tools have all the specific and special features that a company needed for monitoring its network. It is free. And if you the REST API complex, then there are abundant manuals available to help you.
#9. Spiceworks Network Monitor
Spiceworks has developed its name b self as it is the best network management software available today. It monitors and gives real-time data of your network through SNMP. Even if you are a new user, then also you will find installation easy, but it takes your time as it is the initial process of setting up. Once you are done with the setup, you will have a shortcut for the web GUI.
The network maintains a user-friendly design; there is the main dashboard which can be customized. Network Monitor supports color-coded graphs to display the data in an understandable form. From your home screen, you can monitor all your main device.
User configured alerts are another feature where the user can set alert parameters to notify by email or SMS. One can also set the individual alert, but it is said that custom alerts are not advisable as it has higher chances of error. It has an advertisement which is the main limitation of it.
It is the first choice for organizations of all sizes. It supports all versions of Windows. What you need is the download the software on your device.
#10. Advanced IP Scanner
Advanced IP Scanner has about 30 million users worldwide, and the number of users is enough to say that it is one of the top network management software. It uses LAN environments and lets you monitor your network. Many other features like the ability to switch computers on and off remotely, Mac address detection, etc. that make this software popular.
Advanced IP Scanner is swift and lightweight. Within the user-defined range, it scans all IP addresses. Network devices identified automatically, and you can find they are active or not. You save the favorite devices and look them in privacy. Thus IP Scanner is suitable for all companies.
It is easy to use and if you don’t want to define the Ip range, then don’t do it. What you have to do is click on the scan option and the program will start scanning the device of your network and report you. To get more information, right-click on the device.
The major limitation of the Advanced IP Scanners is the user interface. Though it is easy to use yet, it does not have a modern GUI. You can’t create graphs or other visuals, but you can export the scan documents in CSV format.
At last with the limitations, Advanced IP Scanner can work with high-level enterprise environments. And it is entirely free to use.
#11. Logic Monitor
Logic Monitor is an excellent top network monitoring tools, and once you start using it, you can feel it. It automatically discovers devices on your network and collects information about it. Ease of use is another great thing about the software. There are approx. 1000 Logic Modules that automate monitoring and alerts and help the user. Ou can monitor AWS, Azure, apps, servers, and websites from one interface.
Logic Monitor has a lot to offer regarding visualization. You can transfer the data network and display it into color-coded graphs. By one graph, you can view multiple devices. Overall infrastructure, performance, and health display on the main dashboard.
One interesting feature is built-in forecasting like in the left bottom of the image above; you can see the graphs that show you disk usage forecasting. It shows you how much disk can expect to the usage in the future.
For Logic Monitor, there are pricing options also available and named as Starter, Pro, and an Enterprise. The Starter version includes alerting, dashboards, and reporting with a data retention period of three months, alert history storage of three months and ten services of web service checks. The Enterprise version has all the above features for two years and a service check for 300 services with 24×7 support. For the license version, you have to request a quote. It provides you with a free trial of 14-days.
#12. EventSentry
Over the past few years, EventSentry gaining attraction. Regarding action, it is limited to Windows devices. It takes approximately 30 minutes to set up and run. To run it, you don’t have to complete the configuration, and it does not make it inconvenient. The new version lets the user measure bandwidth utilization and view NetFlow data. It easily identifies the connection and its health.
All of your network data converted to charts and graphs by visual displays and a geographical location, you can map network traffic also. All these graphs and displays identify the live network activity from a snapshot instead of the navigation tree.
For the larger enterprises, it supports scheduled reporting. After generating the report, it automatically sends emails to key users. It means once the network finds an error, you can send the report to your team member immediately so that they can help to find a solution.
EventSentry also has pricing options for NetFlow Licenses, full licenses to Network Device Licenses. Pricing of Full license is $85 per year, per Windows device, for 100 licenses $4698 and 1000 devices $28998. It also provides a 30-day free trial.
Conclusion:
It is all about network monitoring software comparison. We hope you find it useful and informative. So before you pick any of the software, try a trial version and choose accordingly. Thank you for reading and stay connected with Top IT Software.
Way back in 2015, we reviewed the must-have top free networking tools. And honestly, those reviews have stood the test of time. But now that time has passed, the landscape has changed, and we think it’s worthwhile to review those old choices and possibly add a few new ones.
Laying the Foundation
To build a network, you start with an architecture, draw the design, and analyze and choose the hardware that meets your requirements. Because many organizations need their network to be up and functioning to generate revenue, having the right set of tools to monitor and manage the one you so lovingly created is critical.
But how do you find the best network monitoring tools when there are hundreds of commercial products, freeware tools, and open-source software to choose from? While the debate about free versus commercial goes on, there are tried and tested, free network monitoring tools that many network admins swear by. Below, we will share some of our favorites with you.
But first…
Open-source choices are good and can even match commercial tools, but you should know that using open-source monitoring requires a high level of involvement with the tool, which may not perfectly suit your needs. As the saying goes, “Open-source is only free if your time is worthless.”
Open-source monitoring solutions often require a significant investment in time and resources. Missing features may have to be built with the help of community support or an in-house IT team. The second consideration is security, which may become an issue, depending on the tool you select and your enterprise’s security guidelines. Additionally, immediate custom fixes may not be available unless you spend time developing and maintaining them yourself.
If you’re looking for a robust yet affordable network monitoring tool offering a greater degree of automation and insight and a lesser degree of required manual input than an open-source solution, SolarWinds® ipMonitor® may be a good option for you. ipMonitor offers scalable network monitoring for your entire network in an easy-to-use, lightweight, and fast solution designed to help minimize downtime and the amount of time you need to spend monitoring your network by hand.
The tool’s Startup Wizard guides you through the processes of alert configuration and automated discovery so you can quickly start getting insights into your network. ipMonitor even offers out-of-the-box recommendations for what you should be monitoring on each of your applications and devices.
One reason someone may want to use a free network monitoring solution is because they’re intimidated by a paid solution. In fact, paid network monitoring tools are typically much easier to use than their free counterparts. This is certainly true when it comes to ipMonitor, as the user-friendly interface helps you quickly identify current (and even potential) issues so you can get to the bottom of them before they cause even more problems for your network performance. ipMonitor helps ensure you never miss anything with its powerful, configurable alerting system. With more than a dozen different notification types built in, ipMonitor helps you make sure the right people on your team know about potential problems as soon as the tool detects them.
ipMonitor is an affordable option for businesses of any size, but if you aren’t sure whether you want to commit to a paid tool, you can try out a free 14-day trial to see if the tool is a good fit for your needs.
When we need a network monitoring tool that is easy to install, and supports monitoring and reporting out of the box, we like SolarWinds® Network Performance Monitor (NPM). NPM acts as a single pane of glass to provide complete and comprehensive network monitoring capabilities that complement some of the essential free tools you may already use.
Knowledge Base
Because enterprise networks are becoming bigger and more complex, it’s important to put network monitoring and managing solutions in place early in the implementation phase.
What’s on the list?
If you do decide to go the free/open-source route, you should check out the following. It’s our list of the best free network monitoring tools available today.
Nagios Core
Nagios® is the great-grand-daddy of monitoring tools, with only ping being more ubiquitous in some circles.
Nagios is popular due to its active development community and external plug-in support. You can create and use external plugins in the form of executable files or Perl® and shell scripts to monitor and collect metrics from every hardware and software used in a network. There are plugins that provide an easier and better GUI, address many limitations in the Core®, and support features, such as auto discovery, extended graphing, notification escalation, and more.
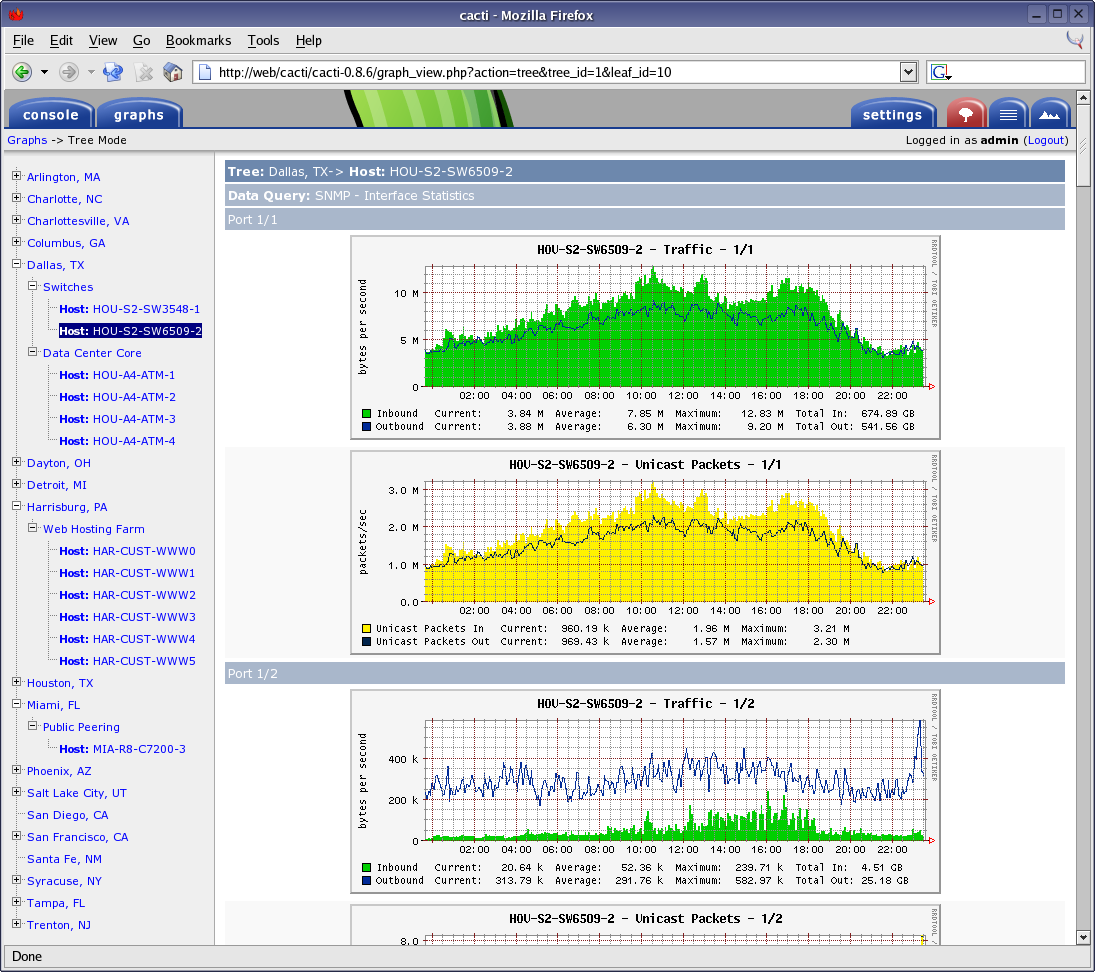
Cacti
Cacti® is another of the monitoring warhorses that has endured as a go-to for network monitoring needs. It allows you to collect data from almost any network element, including routing and switching systems as well as firewalls, and put that data into robust graphs. If you have a device, it’s possible that Cacti’s active community of developers has created a monitoring template for it.
Cacti supports SNMP polling, which itself covers a wide range of network devices. You can also extend Cacti’s capabilities to use scripts, queries, or commands for data collection, and save it as a template to use for polling other devices for similar datasets. Cacti leverages the power of RRDTool, an open-source data logging and graphing system for creating graphs from the stored datasets. RRDTool’s data consolidation lets you store collected data forever and is limited only by the size of your storage. Cacti also allows you to add multiple users and give them access with or without edit permissions, which is perfect for service providers and enterprises with a large NOC team.
Zabbix
Admittedly complex to set up, Zabbix® comes with a simple and clean GUI that makes it easy to manage, once you get the hang of it. Zabbix supports agentless monitoring using technologies such as SNMP, ICMP, Telnet, SSH, etc., and agent-based monitoring for all Linux® distros, Windows® OS, and Solaris®. It supports a number of databases, including MySQL®, PostgreSQL™, SQLite, Oracle®, and IBM® DB2®. Zabbix’s VMware® monitoring capabilities allow you to customize using any scripting or programming language, which is widely regarded as its best feature.
Zabbix is probably the most widely used open-source network monitoring tool after Nagios.
ntop
ntop, which is now ntopng (ng for next generation), is a traffic probe that uses libpcap (for packet capture) to report on network traffic. You can install ntopng on a server with multiple interfaces and use port mirroring or a network tap to feed ntopng with the data packets from the network for analysis. ntopng can analyze traffic even at 10G speeds; report on IP addresses, volume, and bytes for each transaction; sort traffic based on IP, port, and protocol; generate reports for usage; view top talkers; and report on AS information. This level of traffic analysis helps you make informed decisions about capacity planning and QoS design and helps you find bandwidth-hogging users and applications in the network. ntopng has a commercial version called ntopng pro that comes with some additional features, but the open-source version is good enough to quickly gain insight into traffic behavior. ntop can also integrate with external monitoring applications such as Nagios for alerting and provide data for monitoring.
ntopng has some limitations, but the level of network traffic visibility it provides makes it well worth the effort.
Icinga
Built on top of MySQL and PostgreSQL, Icinga is Nagios backwards-compatible, meaning if you have an investment in Nagios scripts, you can port them over with relative ease.
Icinga was created in 2009 by the same group of devs that made Nagios, so they knew their stuff. Since then, the developers have made great strides in terms of expanding both functionality and usability since then. As the Nagios pedigree might imply, its primary focus is monitoring infrastructure and services.
Spiceworks
Spiceworks offers many free IT management tools, including inventory management, help desk workflow, and even cloud monitoring, in addition to the network monitoring solution I’m focusing on here. Built on agentless techniques like WMI (for Windows machines) and SNMP (for network and *nix systems), this free tool can provide insights into many network performance issues. You can also set up customizable notifications and restart services from within the app.
Note that Spiceworks is free because most of its revenue comes from the sale of ad displays in its network. It’s a small price to pay for a free solution, but it’s something to think about before you install.
Observium Community
Observium follows the “freemium” model that is now espoused by most of the open-source community—a core set of features for free, with additional options if you pay for them. While the “Community” (i.e., free) version supports an unlimited number of devices, Observium is still careful to say that it’s meant for home lab use. This is bolstered by the fact that the free version cannot scale past a single server. Run this on your corporate network at your own risk!
The free version also enjoys a 6-month patch and update cycle. If you want fixes any faster than twice a year, you’ll have to pay for them. One of the most painful features held back from the free version is the lack of alerting capabilities. Those caveats aside, you get a full auto-discovery of your devices and metrics (using SNMP and standard protocols, as usual).
Related Top Tools for Network Monitoring
There are a few tools that aren’t monitoring solutions per-se but are so incredibly useful to the monitoring professional that we didn’t feel right leaving them out.
Wireshark
Wireshark® is an open-source packet analyzer that uses libpcap (*nix) or winpcap (Windows) to capture packets and display them on its graphical front-end, while also providing good filtering, grouping, and analysis capabilities. It lets users capture traffic at wire speed or read from packet dumps and analyze details at microscopic levels. Wireshark supports almost every protocol, and has functionalities that filter based on packet type, source, destination, etc. It can analyze VoIP calls, plot IO graphs for all traffic from an interface, decrypt many protocols, export the output, and lots more.
Wireshark provides unlimited opportunities to study packets, which makes it a solid go-to for network, system, and security admins.
Nmap
Nmap uses a discovery feature to find hosts in the network that can be used to create a network map. Network admins value it for its ability to gather information from the host about the Operating System, services, or ports that are running or are open, MAC address info, reverse DNS name, and more.
Scalability is the other big reason why network admins love Nmap. It can scan a single host or an entire network with “hundreds of thousands” of machines.
When you need to quickly map the hosts in your network, Nmap is your tool.
Free Network Monitoring Tools
Most of the tools we’ve focused on in this post have been of the “freemium” variety—a limited set of features (or support) for free, with additional features, support, or offerings available for a cost.
But there is a whole other class of tools which are just free-free. They do a particular task very well, and there is no cost (with the exception of the odd pop-up ad during installation). We wanted to take a moment to dig into a few of the tools that are in “network_utilities” directories on our systems and frequently use.

Also, we want to be clear that the list below isn’t meant to be (or even appear) exhaustive. There are many, MANY useful free network monitoring tools out there, and which ones an IT pro uses is often up to personal preference or the specifics of their work environment. We’re listing out the ones we’ve found in our travels and use often.
Traceroute NG
Ping is great. Traceroute is better. But both fall short in modern networks (and especially with internet-based targets because the internet is intrinsically multi-path). A packet has multiple ways to get to a target at any moment. You don’t need to know how a SINGLE packet got to the destination; you need to know how ALL the packets are moving through the network across time. Traceroute NG does that and avoids the single biggest roadblock to ping and traceroute accuracy—ICMP suppression—at the same time.
Bandwidth Monitor
If you are doing simple monitoring, the first question you’re going to want to know is, “is it up?” Following closely on the heels of that is, “how much bandwidth is it using?” Yes, it’s a simplistic question and an answer that may not really point to a problem (because let’s be honest, a circuit that’s 98% utilized most of the time is called “correctly provisioned” in our book), but that doesn’t mean you don’t want to know. This tool gets that information quickly, simply, and displays the results clearly.
Response Time Viewer for Wireshark
We mentioned Wireshark over in the non-monitoring monitoring tools section because of its flexibility, utility, and ubiquity. But the “-ity” that was left out was “simplicity.” That sucker can be HARD to learn to use, especially for new network engineers fresh on the job. This utility will take Wireshark data and parse it out to show some important statistics simply and clearly. Specifically, it collects, compares, and displays the time for a three-way-handshake versus the time-to-first-byte between two systems. Effectively, it shows you whether a perceived slowdown is due to the network (three-way handshake) or application response (time to first byte). This can be an effective way to narrow down your troubleshooting work and focus on solving the right problem faster.
IP SLA Monitor
IP SLA is one of the most often-overlooked techniques in a monitoring specialist’s arsenal. Relegated to being “that protocol for VoIP,” the reality is that IP SLA operations can tell you much more than jitter, packet loss, and MOS. You can test a remote DHCP server to see if it has addresses to hand out, check the response of DNS from anywhere within your company, verify that essential services like FTP and HTTP are running, and more.
Free Network Monitoring Tools For Mac Os
So, this free tool is something of a secret weapon for engineers who need to get miraculous tasks done on the cheap.
Free Network Monitoring Tools For Macbook Pro
What have we learned?
Network Tools For Mac
This year, monitoring professionals have almost an embarrassment of riches when it comes to free and open-source solutions to help us do our jobs. While none of these free tools are exactly push-button simple to install, maintain, or use, if your budget for tools is close to non-existing and you have the time to invest, they may fit the bill. Otherwise, we’d recommend using a tool like SolarWinds NPM, which is easy to install and supports motioning and reporting right out of the box.